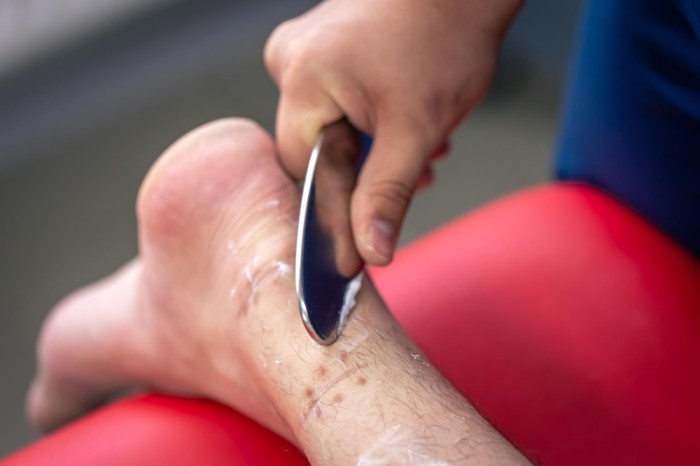
Diabetic foot ulcers are a serious complication affecting millions of individuals with diabetes worldwide. These open sores, typically appearing on the bottom of the foot, toes, or heels, can significantly impact mobility and quality of life if not managed properly. Poor circulation, nerve damage, and elevated blood sugar levels make people with diabetes particularly susceptible to foot ulcers.
Implementing best practices in diabetic ulcers on feet treatment is crucial for promoting faster recovery, preventing infections, and minimizing the risk of severe complications such as amputation. With advancements in medical care, modern treatment approaches now combine expert assessment, advanced wound care, preventive strategies, and patient education to achieve optimal outcomes.
Understanding Diabetic Foot Ulcers
A diabetic foot ulcer is an open sore or wound that develops as a result of various diabetes-related complications:
-
Peripheral neuropathy: Nerve damage reduces sensation, making injuries go unnoticed and delaying treatment.
-
Poor circulation: Limited blood flow slows the body’s natural healing process.
-
Foot deformities: Conditions such as bunions, hammertoes, or flat feet create pressure points prone to ulcers.
-
High blood sugar levels: Hyperglycemia impairs immune function and tissue repair, prolonging healing.
Understanding these factors is key to implementing safe and effective diabetic ulcers on feet treatment strategies.
Early Signs and Symptoms
Early detection is critical to prevent serious complications. Common warning signs of diabetic foot ulcers include:
-
Redness, swelling, or warmth around the affected area
-
Persistent sores, blisters, or cuts that fail to heal
-
Discharge, pus, or foul odor from the wound
-
Pain, tenderness, or numbness
-
Changes in skin color, texture, or thickness
Routine foot inspections and regular medical checkups allow for timely intervention and significantly improve recovery outcomes.
The Importance of Following Best Practices
Applying best practices in diabetic ulcers on feet treatment ensures:
-
Faster and more effective wound healing
-
Reduced risk of infections and systemic complications
-
Prevention of chronic wounds and recurrence
-
Preservation of mobility and independence
-
Improved overall quality of life
A structured, evidence-based approach is essential to maximize healing and minimize complications.
Core Best Practices in Treatment
1. Comprehensive Wound Assessment
The foundation of effective treatment is a thorough assessment by a healthcare professional:
-
Measure wound size, depth, and severity
-
Examine for signs of infection or necrotic tissue
-
Evaluate circulation, nerve function, and pressure points
-
Identify deformities or underlying conditions contributing to ulcer formation
A detailed assessment allows healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to the patient’s needs.
2. Infection Control
Infections are a major complication and can severely delay healing. Best practices include:
-
Topical antibiotics for minor localized infections
-
Oral or intravenous antibiotics for more severe infections
-
Laboratory cultures to select the most effective antibiotic
-
Continuous monitoring for early signs of systemic infection
Early and precise infection management reduces the risk of cellulitis, osteomyelitis, and sepsis.
3. Debridement and Wound Cleaning
Debridement involves removing dead or infected tissue to create an optimal healing environment:
-
Eliminates necrotic tissue that can harbor bacteria
-
Prepares the wound for advanced therapies and dressings
-
Stimulates tissue regeneration and promotes faster healing
Advanced wound dressings, such as hydrocolloids, foam dressings, and antimicrobial coverings, help maintain moisture balance and protect the wound from contaminants.
4. Pressure Offloading
Reducing pressure on the ulcer is vital to promote healing:
-
Custom diabetic shoes or orthotic inserts redistribute weight evenly
-
Total contact casts relieve pressure and protect the ulcer
-
Mobility aids, such as crutches or specialized boots, may be used for severe ulcers
Pressure offloading prevents further tissue damage and allows the wound to heal more efficiently.
5. Blood Sugar Management
Maintaining optimal blood glucose levels is a cornerstone of ulcer recovery:
-
Continuous glucose monitoring for real-time tracking
-
Personalized insulin or medication therapy
-
Nutritional counseling to stabilize blood sugar levels
-
Regular exercise to improve circulation and overall health
Proper blood sugar control accelerates wound healing and reduces the risk of recurrence.
6. Advanced Wound Care Therapies
Innovative therapies have revolutionized diabetic ulcers on feet treatment, including:
-
Negative Pressure Wound Therapy (NPWT): Uses suction to remove fluid, reduce swelling, and stimulate tissue regeneration
-
Growth Factor Therapy: Enhances cellular repair and promotes faster healing
-
Bioengineered Skin Substitutes: Supports tissue regeneration for large or chronic ulcers
-
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT): Increases oxygen delivery to tissues, accelerating healing and preventing infection
These treatments, combined with standard care, significantly improve outcomes.
7. Surgical Interventions
Surgery may be necessary for severe or non-healing ulcers:
-
Debridement Surgery: Removes dead or infected tissue
-
Reconstructive Surgery: Corrects foot deformities and redistributes pressure
-
Amputation (as a last resort): Performed only when tissue damage or infection is uncontrollable
Minimally invasive procedures reduce recovery time and complications, providing safer treatment options.
8. Multidisciplinary Care
Expert management involves a team approach:
-
Podiatrists: Specialized in foot care and ulcer management
-
Endocrinologists: Control blood sugar and manage diabetes-related complications
-
Wound Care Specialists: Apply advanced therapies and monitor healing
-
Vascular Surgeons: Address circulation issues
-
Nutritionists: Provide diet plans that promote tissue repair
Collaboration ensures a holistic approach to diabetic ulcers on feet treatment, addressing all factors affecting recovery.
9. Patient Education and Lifestyle Adjustments
Patient involvement is critical for success and faster recovery:
-
Daily foot inspections to detect early signs of ulcers
-
Maintaining foot hygiene and keeping feet dry
-
Wearing protective, well-fitted footwear
-
Avoiding walking barefoot
-
Adopting a healthy diet and active lifestyle
Educated patients adhere better to treatment plans and reduce the risk of complications and recurrence.
10. Preventing Recurrence
Even after healing, diabetic foot ulcers can recur. Best practices to prevent recurrence include:
-
Regular foot screenings and checkups
-
Custom orthotic footwear to reduce pressure points
-
Prompt treatment of minor injuries
-
Maintaining blood sugar control
-
Ensuring overall vascular and foot health
Preventive measures are essential for long-term success in diabetic ulcers on feet treatment.
11. When to Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Certain warning signs require urgent medical care:
-
Rapidly worsening or enlarging ulcers
-
Pus or foul-smelling discharge
-
Red streaks or swelling extending from the wound
-
Fever, chills, or systemic infection symptoms
-
Severe pain or sudden loss of sensation
Prompt intervention prevents infections from spreading and protects limb function.
Benefits of Following Best Practices
Adhering to best practices in diabetic ulcers on feet treatment offers significant advantages:
-
Faster and more reliable wound healing
-
Reduced risk of infections and serious complications
-
Preservation of mobility and independence
-
Improved quality of life
-
Cost-effective long-term care
Modern, evidence-based treatment protocols ensure comprehensive care, addressing both immediate healing and long-term prevention.
Conclusion
Diabetic foot ulcers are a serious complication of diabetes that require expert management and adherence to best practices. Safe and advanced diabetic ulcers on feet treatment combines thorough wound assessment, infection control, pressure offloading, blood sugar management, advanced therapies, surgical interventions when necessary, multidisciplinary care, and patient education.
Early detection, personalized treatment, and preventive strategies accelerate healing, reduce complications, and preserve mobility. By following best practices, individuals with diabetes can recover faster, prevent recurrence, and maintain long-term foot health, ultimately improving their quality of life.